MariaDB est l'un des systèmes de gestion de base de données open source les plus populaires utilisés par les petites et grandes entreprises. Il s'agit d'un fork du célèbre serveur de base de données MySQL, développé par MariaDB Corporation Ab, dirigé par les développeurs originaux de MySQL.
MariaDB est entièrement compatible avec MySQL pour assurer une capacité de remplacement instantané. MariaDB est souvent utilisé comme serveur de base de données dans la pile LAMP et LEMP.
LIRE : Comment installer la pile LAMP sur CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
LIRE : Comment installer la pile LEMP sur CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
Dans cet article, nous verrons comment installer MariaDB sur CentOS 8 / RHEL 8.
Installer MariaDB sur CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
Vous pouvez obtenir des packages MariaDB pour CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 de deux manières.
- Référentiel Red Hat (v10.3)
- Miroir MariaDB officiel (v10.4)
Installer MariaDB à partir du référentiel AppStream
L'installation de MariaDB à partir du référentiel AppStream est simple. Cependant, le référentiel peut avoir une version un peu ancienne du package MariaDB.
yum -y install @mariadb
Installer MariaDB à partir du miroir officiel de MariaDB
La fondation MariaDB propose des packages MariaDB pour CentOS 8 / RHEL 8. Les packages fournis par MariaDB sont toujours frais et pris en charge par la communauté MariaDB.
CentOS 8
cat <<EOF >> /etc/yum.repos.d/mariadb.repo [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.4/centos8-amd64 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1 EOF
RHEL 8
cat <<EOF >> /etc/yum.repos.d/mariadb.repo [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.4/rhel8-amd64 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1 EOF
Installez le serveur MariaDB à l'aide de la commande suivante.
Nous devons désactiver temporairement les référentiels rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms et AppStream sur RHEL 8 et CentOS 8 respectivement pour permettre à yum de télécharger des packages à partir du miroir MariaDB.### CentOS 8 ### yum install -y boost-program-options yum --disablerepo=AppStream install -y MariaDB-server MariaDB-client ### RHEL 8 ### yum --disablerepo=rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms install -y MariaDB-server MariaDB-client
Gérer le service MariaDB
Si vous souhaitez démarrer/arrêter le service MariaDB, vous pouvez utiliser les commandes suivantes.
systemctl start mariadb systemctl stop mariadb
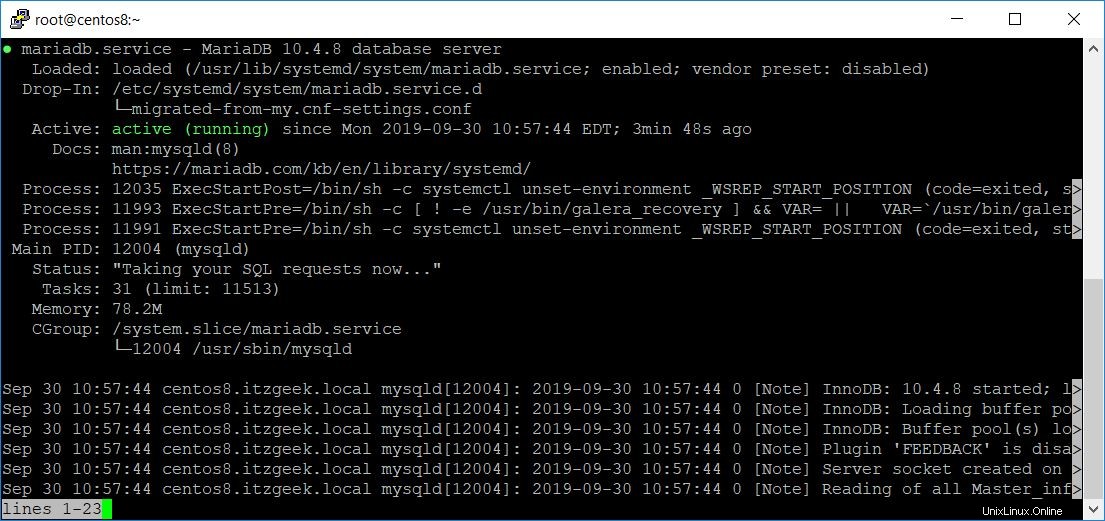
Vérifiez si MariaDB est en cours d'exécution ou non.
systemctl status mariadb
Installation sécurisée de MariaDB
Utilisez la commande mysql_secure_installation pour effectuer la configuration initiale du serveur MariaDB. Il est recommandé d'exécuter cette commande sur les serveurs de production. Il supprime l'utilisateur anonyme, teste la base de données et interdit la connexion root à distance.
mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
haven't set the root password yet, you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none): << Just Press Enter
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password or using the unix_socket ensures that nobody
can log into the MariaDB root user without the proper authorisation.
You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'.
Switch to unix_socket authentication [Y/n] N << Disable Unix Socket Authendication to Enable Password Authentication
... skipping.
You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'.
Change the root password? [Y/n] Y << Set MariaDB root password
New password: << Enter root password
Re-enter new password: << Re-Enter root password
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y << Remove Anonymous user
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y << Disallow root login remotely
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y << Remove test database
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y << Reload privilege tables
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
Accéder à MariaDB
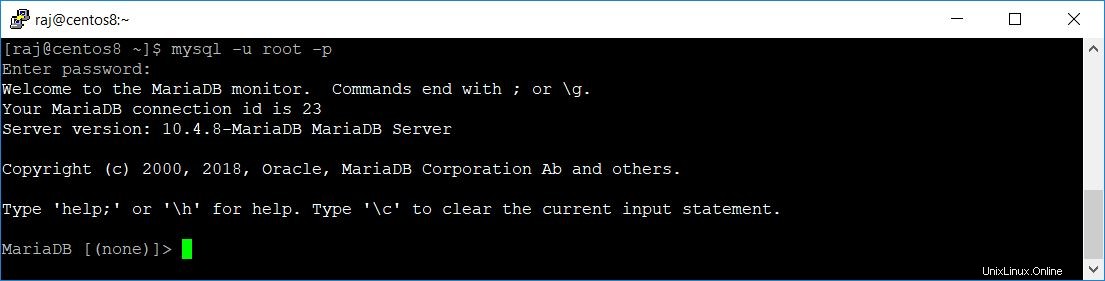
Connectez-vous au serveur MariaDB avec la commande ci-dessous.
mysql -u root -pMot de passe requis
Conclusion
C'est tout. Dans cet article, vous avez appris à installer MariaDB sur CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 et à effectuer la configuration initiale. Lisez les articles MariaDB pour débutants pour en savoir plus sur l'utilisation de MariaDB.